NextGIS software platform, including cloud service nextgis.com, is being used by different industries for a variety of purposes.
Here’s a case study of how NextGIS software platform is used by telecom industry.
Background
Fairwaves deploys affordable mobile networks in third-world countries. Site selection for base stations is an important stage of network deployment as it can not only reduce time and money spent for equipment installation & maintenance but ultimately provide better service for their subscribers.
Previously Fairwaves specialists were using Google Earth for selection of potential sites, and G-NetTrack Pro mobile app for connectivity drive tests after site deployment. Built site locations and drive test results were stored locally and visualized in Google Earth. Other available geodata for site locations (like raster images showing ???) were also stored locally and viewed separately which prevented Fairwaves from deriving its full value. Also no data analysis tools (e.g. digital elevation models and viewsheds) were used to better evaluate area features.
Goals
In Fairwaves case we’ve pursued the following goals:
How NextGIS software platform helped to optimize site selection process:
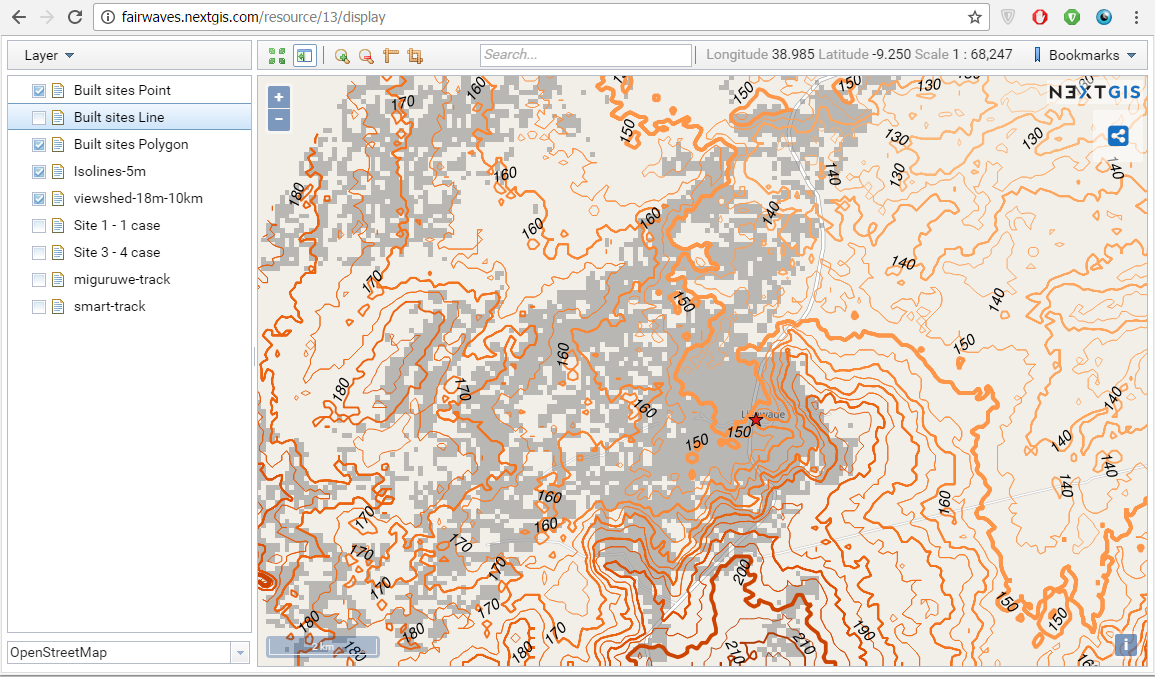
1. First we’ve built digital elevation model (DEM) and elevation isolines for two built sites using NextGIS Geoprocessing – on-demand processing infrastructure which runs various calculations involving spatial data. Together with Fairwaves we formulated requirements and tried different settings to better match their expectations.
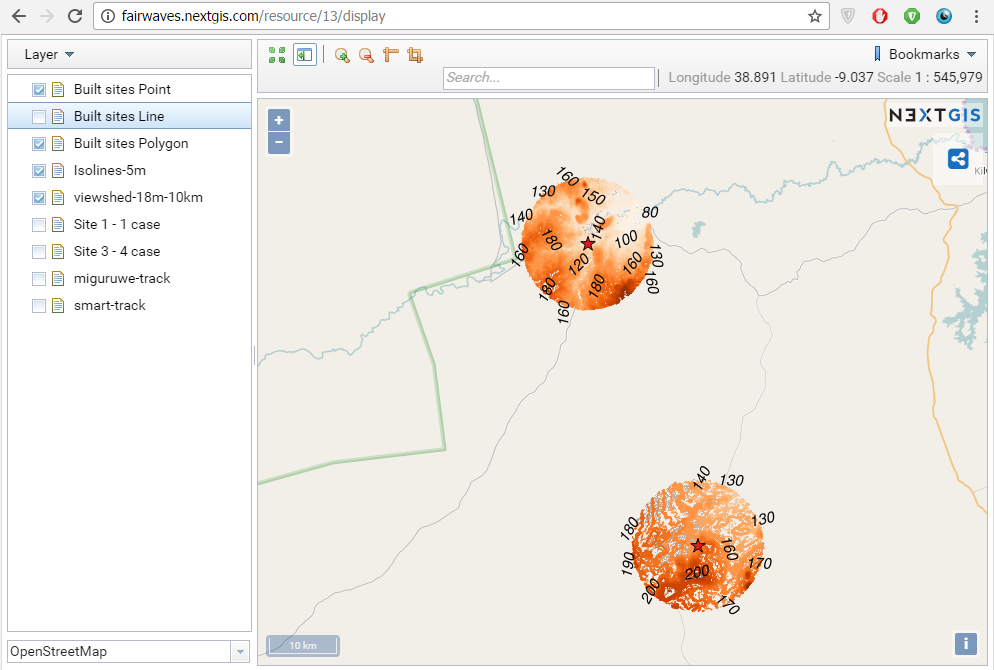
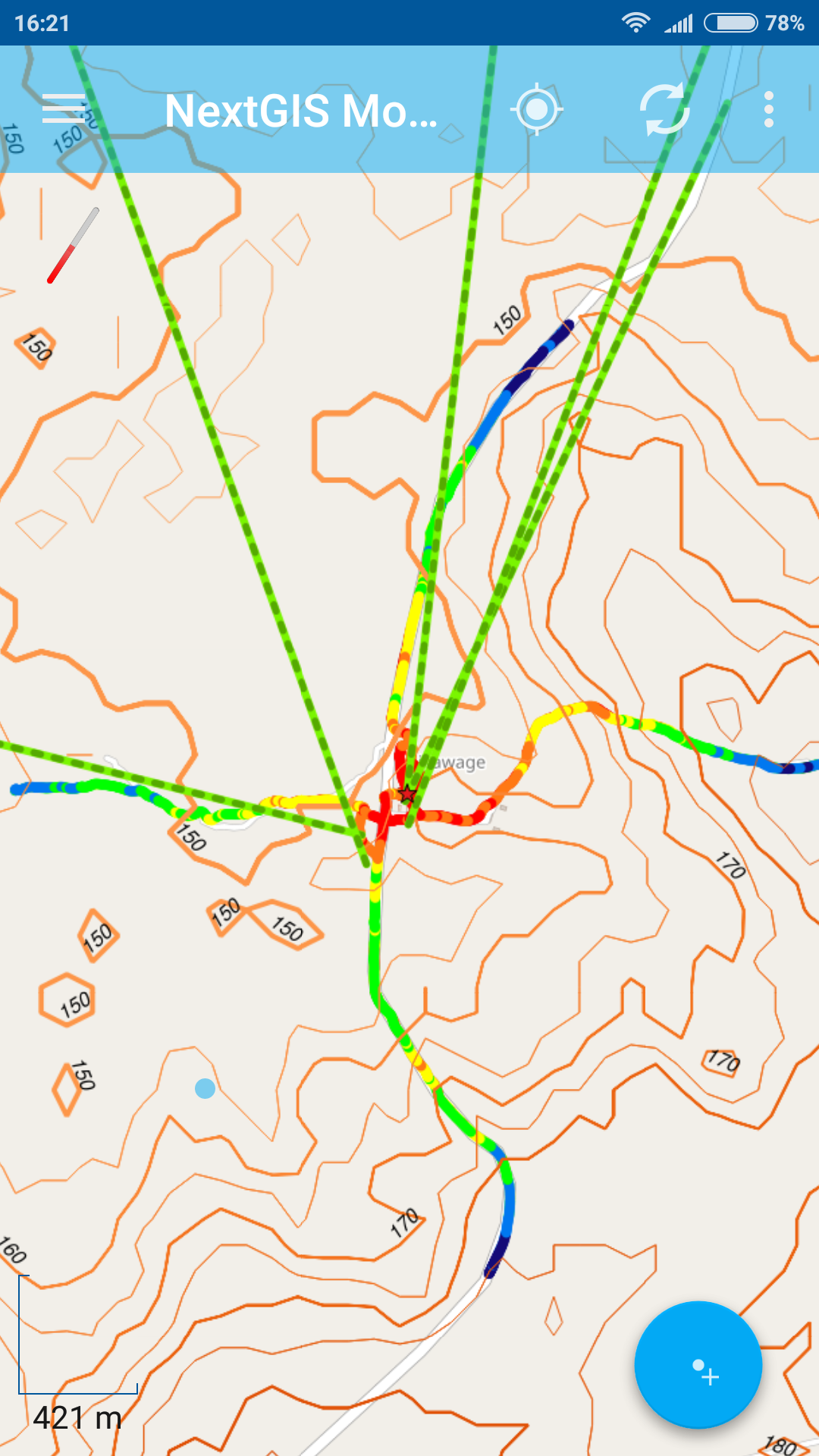
2. Next we’ve calculated viewsheds to assess which areas will be in direct line of sight from each built site. We’ve also tried various parameters to better reflect the area and data density requirements. These manipulations were done using NextGIS QGIS – desktop GIS with powerful styling and data management functions. Being done on the planning stage this simple geodata analysis could provide valuable insight and influence final decision on optimal site location. But even after the sites are built it can be useful – by simplifying drive tests and site optimization process.
3. Styled viewsheds, isolines and sites locations were uploaded in 1 click to nextgis.com cloud service using NextGIS Connect. Now all Fairwaves employees and customers can easily access geodata and maps available for the sites and stay on the same page.
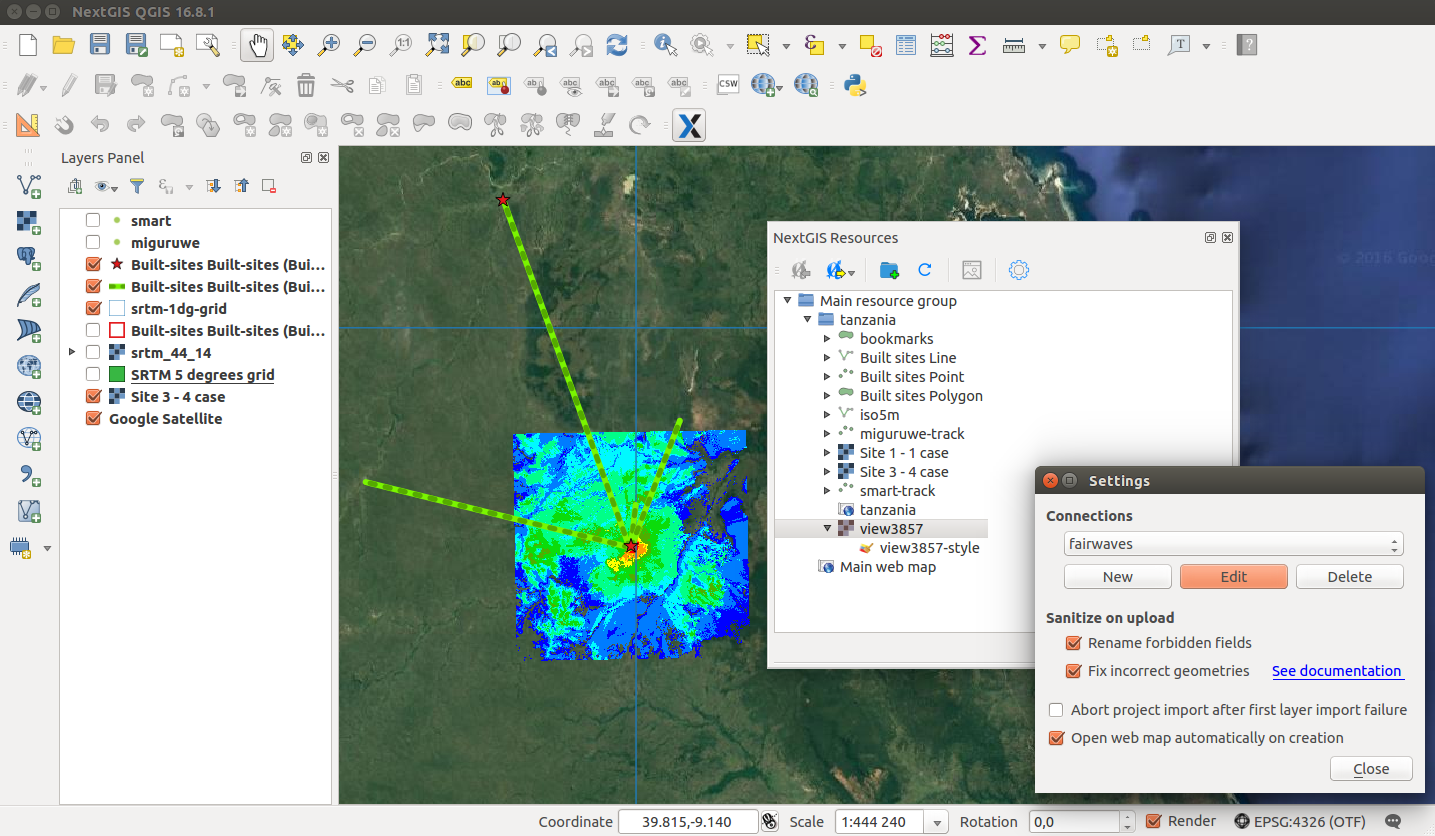
4. Thanks to good integration between desktop and nextgis.com, KML rasters from NAME OF THE SOFTWARE showing ??? were automatically imported to the same web map…
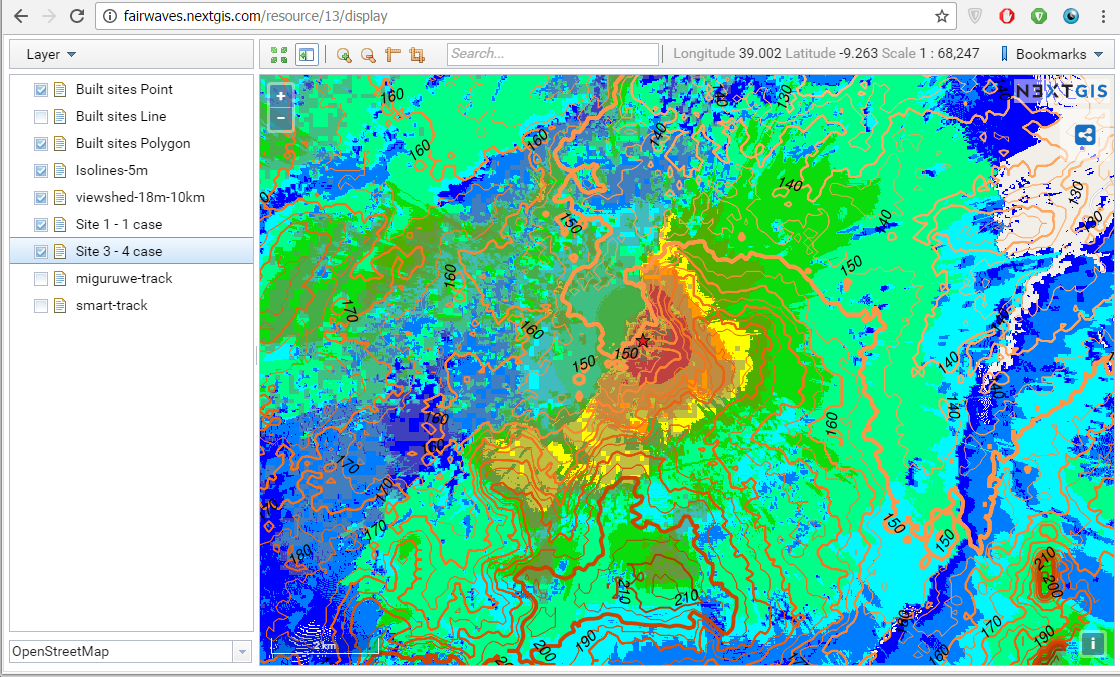
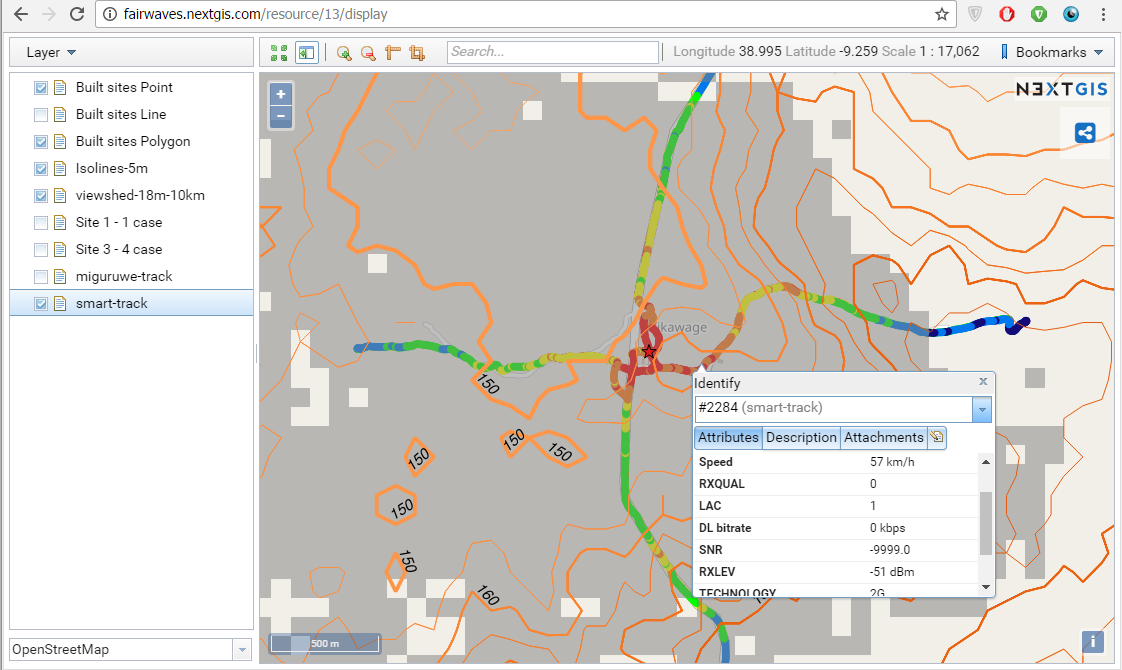
5. …As well as results of connectivity drive tests.
6. We’ve also optimized data layers structure for easier work with web map.
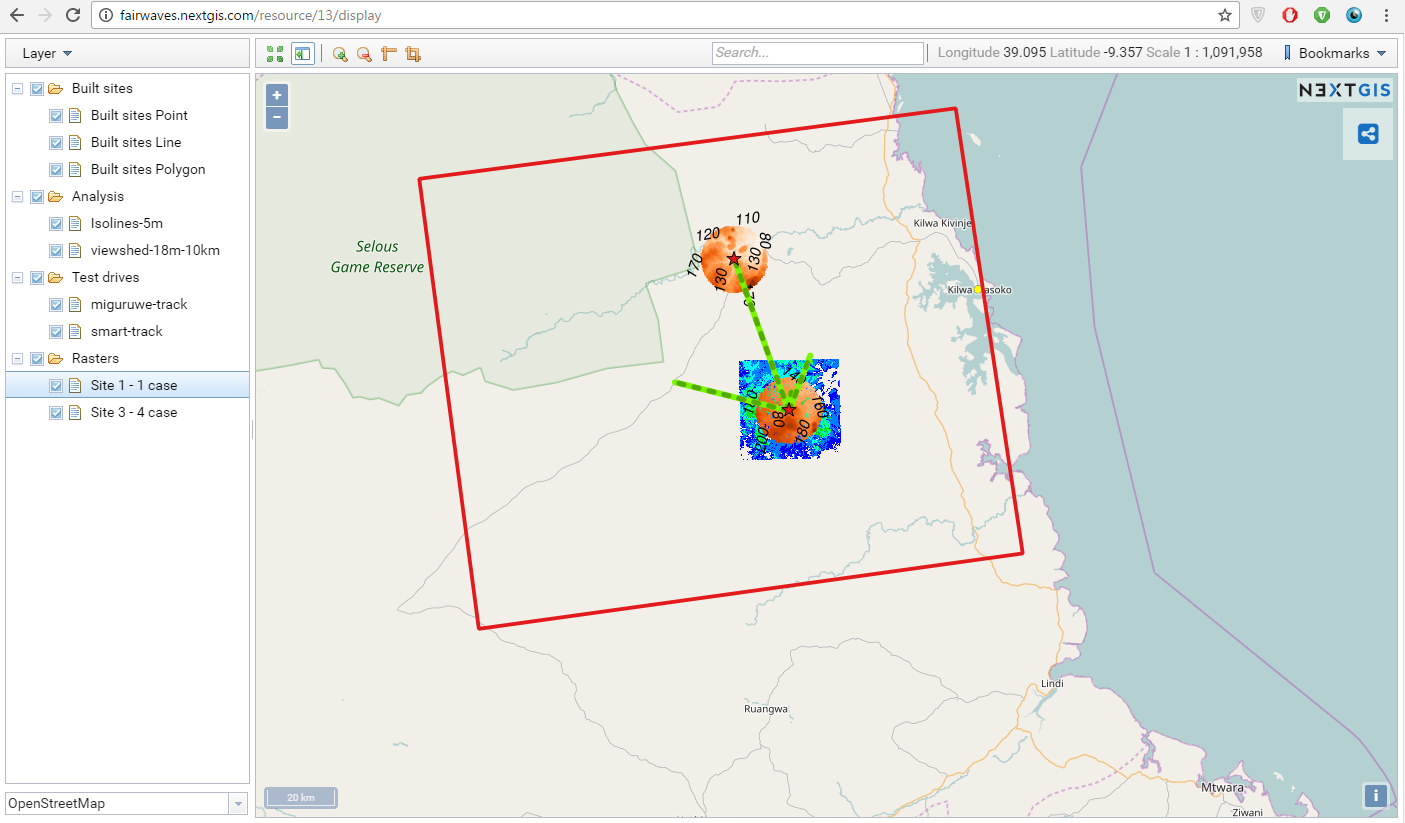
7. Since Fairwaves is our Premium user all their nextgis.com data layers and web maps are private. Using permissions management settings they can provide different level of access to different people according to their business needs (e.g. each customer can see only one site/site cluster or only certain data layers but not the others).
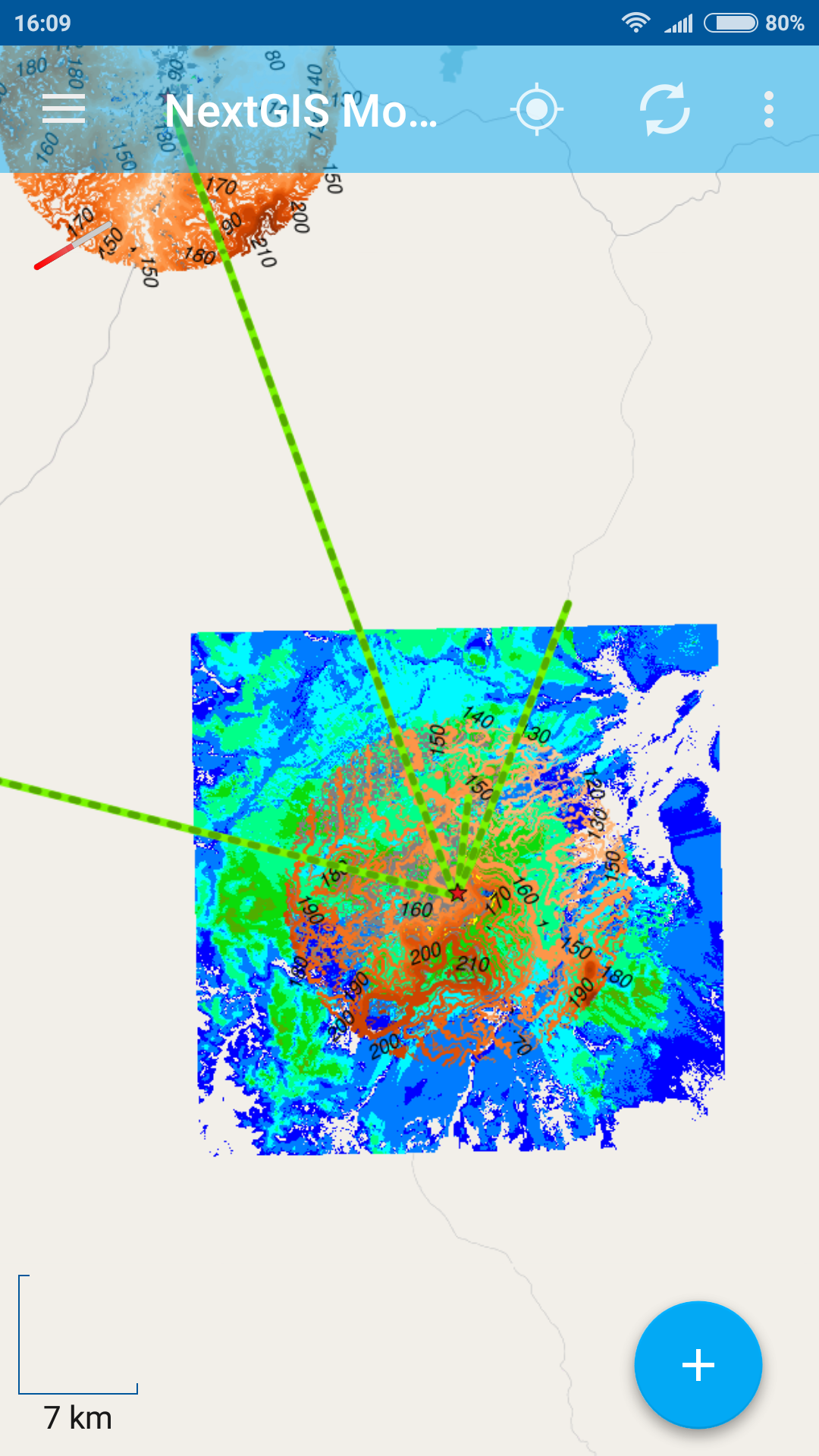
8. All resulting webmaps and data layers became immediately available for viewing and editing in NextGIS Mobile – GIS for smart devices which connects to nextgis.com and able to receive and send data to it.
 |
 |
How else NextGIS software platform can serve telecom industry?
NextGIS geospatial software runs on desktop, server, web and mobile and can be used for other needs of telecom industry, including: